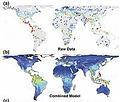
 一份關於全球植物多樣性分布的地圖,顯示出氣候變遷對於人類食用植物可能帶來的影響。繪製這份地圖的科學家表示,當中觀測到的植物數量高達數百萬種,為迄今規模最大的一項研究成果。
一份關於全球植物多樣性分布的地圖,顯示出氣候變遷對於人類食用植物可能帶來的影響。繪製這份地圖的科學家表示,當中觀測到的植物數量高達數百萬種,為迄今規模最大的一項研究成果。
加州大學聖地牙哥校區教授傑玆(Dr. Walter Jetz)與波昂大學生物學家克雷夫特(Holger Kreft)在這份繪圖研究中探究,如何能單就以環境條件來預測植物物種的多樣性。這份地圖並標示出全球1千餘處地理區域中,植物物種型態的多樣。
埋首於波昂大學植物多樣性研究所的克雷夫特表示,「在氣候變遷的影響下,某些具有重要療效的植物在我們發現它們之前,可能就已經消失了。在我們所做的生態研究中,就包含了複合式的多樣性,例如全球的環境關係可能透過規模小但很重要的方式,提供協助,以避免犯下無可挽救的錯誤。」
A new global set of maps of plant diversity offers clues to the likely impact of climate change on the services plants provide to humans. With several hundred thousand plant species plotted, the scientists who created the maps say they are the most extensive to date.
Dr. Walter Jetz of the University of California-San Diego and Holger Kreft of the University of Bonn sought in their mapping study to determine how well the diversity, or the "richness," of plant species could be predicted from environmental conditions alone. The maps depict the species richness patterns of plants in 1,032 geographic regions worldwide.
"Climate change may drive to extinction plants that hold important cures before we find them," says Kreft, a biologist at the Nees Institute for Biodiversity of Plants at the University of Bonn. "Ecological research like ours that captures complex diversity - environment relationships on a global scale may assist in a small, but important way so that such a fatal potential failure can be averted," said Kreft.
全文及圖片詳見 ENS報導







