世界五大海洋環流垃圾湯 科學家將調查
 加州海洋科學家夫妻檔馬庫斯‧艾立克森博士(Dr. Marcus Eriksen)與安‧庫密斯(Anna Cummins)2月4日將自百慕達啟程,紀錄北大西洋環流塑膠污染的範圍。北大西洋環流是北大西洋中洋流所構成的渦流。研究團隊將搭乘72英尺長的單桅帆船海龍號,橫越馬尾藻海(Sargasso Sea),抵達亞速群島。
加州海洋科學家夫妻檔馬庫斯‧艾立克森博士(Dr. Marcus Eriksen)與安‧庫密斯(Anna Cummins)2月4日將自百慕達啟程,紀錄北大西洋環流塑膠污染的範圍。北大西洋環流是北大西洋中洋流所構成的渦流。研究團隊將搭乘72英尺長的單桅帆船海龍號,橫越馬尾藻海(Sargasso Sea),抵達亞速群島。
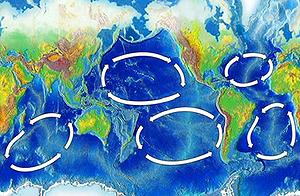
此研究團隊率先對全球五個大洋環流中逐漸累積的塑膠物質進行研究。環流由風與洋流所形成,分別位於南大西洋、北大西洋、南太平洋、北太平洋與印度洋。
棄置於陸上或海中的食物與飲水塑膠容器、玩具、塑膠袋、釣魚線與網具,在這些大洋環流中永無止盡地漂浮並打轉,碎裂成愈來愈小的碎屑,但永遠不會完全消失。
「我們現在要研究的問題──塑膠顆粒表面上的化學物質是否會藉由攝食而進入魚類身體組織,進而進入食物鏈中,最終出現在我們的餐桌上?」艾立克森夫婦說道。
艾立克森說:「塑膠顆粒在海中會如同吸引化學物的磁鐵,吸引如DDT, 多氯聯苯、阻燃劑與其他污染物。」
「塑膠顆粒可吸收無法與水混合的『疏水性』化學物質,而不能吸收『親脂性』物質,意即吸引油性物質,如以石油為原料的塑膠物。」艾立克森解釋。
「諸如DDT, 多氯聯苯、阻燃劑、殺蟲劑與其他疏水性的持久性有機污染物會被塑膠顆粒吸附,達到高濃度─相當於周遭海水濃度的100萬倍。」
「這是塑膠污染物能影響人類之所在。我們在魚隻腹部發現塑膠顆粒,其可能把塑膠當做食物,又或者垃圾堆吸引魚隻前來產卵、藤壺成長其上。」
研究團隊目前正航行於馬尾藻海,冬季風浪較大,但夏天會有颶風將更危險。
艾立克森夫婦於大西洋上,首次將採集拖網放入水中,不久便蒐集到塑膠廢棄物。其採集到碎裂的塑膠膜、一個牛奶罐瓶蓋邊環、幾段塑膠彩帶,以及塑膠粒(nurdle),意即塑膠產品製程中的細小塑膠樹脂顆粒。美國一年至少生產2700萬噸的塑膠粒。
海洋塑膠對人類健康的潛在影響仍屬未知數,科學家預估近半數海鳥種類、所有的海龜種類,以及22種海洋哺乳類均遭受塑膠廢棄物的危害,或因此致命,不管是經由攝食,或是在塑膠垃圾分解成微小碎末之前遭到纏繞與勒斃。
此計畫相關訊息請參閱計畫網站
Marine scientists set sail from Bermuda on Thursday to document the extent of plastic pollution in the North Atlantic Gyre, a swirling vortex of ocean currents in the northern Atlantic Ocean. The scientists and crew are aboard the 72-foot sloop Sea Dragon sailing across the Sargasso Sea to the Azores Islands.
The husband and wife team of California researchers, Dr. Marcus Eriksen and Anna Cummins, are the first to study the plastics that accumulate in all of the world's five oceanic gyres. The gyres are formed by winds and currents in North and South Atlantic, the North and South Pacific and the Indian oceans.
In these gyres, plastic food and water containers, toys, plastic bags, six-pack rings, condoms, fishing lines and nets discarded on land or at sea float and whirl endlessly, breaking down into smaller and smaller pieces but never completely disappearing.
"The question we're now looking into - do the chemicals on the surface of plastic particles get into the tissues of fish through ingestion, work their way up the food chain, and wind up on our dinner plate?" the Eriksen and Cummins told ENS in an interview.
"Plastic particles at sea act as magnets for chemicals like DDT, PCBs, flame retardants and other pollutants," says Eriksen.
"Plastic particles can absorb chemicals that are "hydrophobic," that is they don't mix with water, but are "lipophilic," that is they are attracted to oily substances, such as petroleum-based plastics," he explains.
"Pollutants like PCBs, DDT, flame retardants, pesticides, and other hydrophobic persistent organic pollutants can stick to plastic particles at high concentrations - up to a million times higher concentration than the seawater around them," Eriksen says.
"This is where plastic pollution can impact humans. We find plastic particles in the stomachs of fish that may mistake plastic for food, or be attracted to fish eggs or barnacles growing on pieces of trash," the scientists said.
Eriksen and Cummins are sailing the Sargasso Sea now because while the seas are rougher in winter, the summer brings hurricanes, a greater danger.
Sailing out into the Atlantic, Eriksen and Cummins dropped their first collection trawl into the water and did not have to wait long for plastic debris to accumulate.
They caught shredded plastic film, a milk jug ring, random pieces of plastic confetti, and nurdles, the scrap plastic resin pellets from production of plastic goods. At least 27 million tonnes of nurdles are manufactured annually in the United States.
While potential human health effects of marine plastic remain unknown, scientists estimate that nearly half of all seabird species, all sea turtle species, and 22 species of marine mammals are harmed or killed by plastic waste, either from ingestion, entanglement or strangulation before the debris has been broken down into tiny fragments.
全文及圖片詳見:ENS






