美國地質調查所(US Geological Survey)2月22日發表一份新報告,指出南極半島南部的冰棚正因氣候變遷而逐漸退縮。此一美國聯邦政府最大的水資源、土地、生物科學與民用製圖機構警告說:「這可能導致冰河退縮與海平面上升,若暖化持續,則會威脅到世界沿海社區與低地島嶼。」
地質調查所的研究是首次對南極半島南部每一個冰鋒(冰棚或冰川溶解的前緣)進行紀錄,這裡的冰鋒自1947年至2009年,在整體上持續退縮,最劇烈的幾次變動發生在1990年之後。
地質調查所科學家珍‧費里諾(Jane Ferrigno)說道:「這份研究屬於地質調查所進行的大型計畫之一部分,此計劃是首次仔細研究整個南極大陸海岸線,這至關重要,因為南極冰層涵蓋地球上91%的冰川冰。」
「冰棚消失是全球暖化影響的證據,」她說:「我們必須有所警覺,要持續去暸解並觀察我們的氣候系統正在如何變化。」
地質調查所先前曾記錄到整個南極半島上的大部分冰鋒也已在20世紀末至21世紀初這段期間內有所消退。
冰棚是與大陸相連但已經漂浮在水面上的冰層,與南極冰層相接。南極大陸上有98%的面積為冰層所覆蓋。當冰棚破裂,會讓冰層更易透過冰川河口與冰流(ice streams)流入大海。冰由陸地移轉到海洋中,則會使海平面上升。
地質調查所表示,南極半島是南極改變最為快速的區域,因為這裡距離南極點最遠。若是地球持續暖化,這裡的冰層消退可能得以預測南極和世界其他部分的情況。
半島南部的消退狀況特別受到注意,是因為該區域測得半島的最低溫,顯示出全球暖化正影響整個半島。
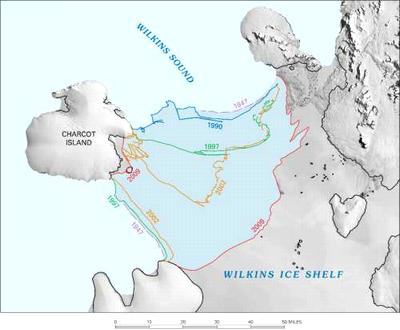
南極半島西側的威爾金斯(Wilkins)冰棚在2008年曾有過大規模的崩解。在2009年初,冰棚與沙科島(Charcot)鄰近的海山邊緣之間仍有一條狹窄的冰橋相連結。這座冰橋在2009年4月斷裂。
Ice shelves are retreating in the southern section of the Antarctic Peninsula due to climate change, the U.S. Geological Survey announced today in a new report. "This could result in glacier retreat and sea-level rise if warming continues, threatening coastal communities and low-lying islands worldwide," warns the federal government's largest water, earth, biological science and civilian mapping agency.
USGS research is the first to document that every ice front in the southern part of the Antarctic Peninsula has been retreating overall from 1947 to 2009, with the most dramatic changes occurring since 1990.
"This research is part of a larger ongoing USGS project that is for the first time studying the entire Antarctic coastline in detail, and this is important because the Antarctic ice sheet contains 91 percent of Earth's glacier ice," said USGS scientist Jane Ferrigno.
"The loss of ice shelves is evidence of the effects of global warming," she said. "We need to be alert and continually understand and observe how our climate system is changing."
The USGS previously documented that the majority of ice fronts on the entire Antarctic Peninsula have also retreated during the late 20th century and into the early 21st century.
The ice shelves are attached to the continent and already floating, holding in place the Antarctic ice sheet that covers about 98 percent of the Antarctic continent.
As the ice shelves break off, it is easier for outlet glaciers and ice streams from the ice sheet to flow into the sea. The transition of that ice from land to the ocean is what raises sea level.
The Peninsula is one of Antarctica's most rapidly changing areas because it is farthest away from the South Pole, and its ice shelf loss may be a forecast of changes in other parts of Antarctica and the world if warming continues, the USGS said.
Retreat along the southern part of the Peninsula is of particular interest because that area has the Peninsula's coolest temperatures, demonstrating that global warming is affecting the entire length of the Peninsula.
The Wilkins Ice Shelf, on the western side of the Antarctic Peninsula, experienced multiple disintegration events in 2008. By the beginning of 2009, a narrow ice bridge was all that remained to connect the ice shelf to ice fragments fringing nearby Charcot Island. That bridge gave way in early April 2009.
全文及圖片詳見:ENS